If you’re wondering what to expect during your second week of pregnancy, you’re not alone. While some women may not experience many symptoms during this time, others are highly in tune with their bodies and can detect early pregnancy signs. In this article, we’ll walk you through the common pregnancy symptoms at two weeks, how your baby is developing, and what you need to know about this early stage of pregnancy.
Early Pregnancy Symptoms at Two Weeks: Signs You Might Be Pregnant
At two weeks pregnant, you may not experience major symptoms, but there are key signs that can indicate you’ve conceived. Here are the common symptoms you may notice:
1. Missed Period
One of the first and most reliable signs that you’re two weeks pregnant is a missed period. If you’ve conceived, your next menstrual cycle will likely be skipped. Keep in mind that some women may experience light bleeding or spotting, which is different from a normal period. This can be a sign of implantation bleeding as the fertilized egg attaches to your uterine lining.
2. Spotting or Implantation Bleeding
Spotting or light bleeding can occur during the second week of pregnancy, usually around the time your fertilized egg implants into the uterine lining. This implantation bleeding is much lighter than your regular period and typically does not last long. It may also be accompanied by mild cramps or digestive discomfort.
3. Fatigue
Fatigue is another common symptom in the early weeks of pregnancy. Even though you might sleep a full night, you may still feel very tired. This tiredness is often due to rising pregnancy hormones (HCG), which double every 24-48 hours during the early stages.
4. Food Cravings and Aversions
Pregnancy hormones can make you crave certain foods or develop strong aversions to others. You may suddenly feel a strong desire for foods you didn’t care for before or lose your appetite for foods you loved. These food cravings and aversions are common during early pregnancy and can start as early as two weeks.
5. Nausea
Morning sickness or nausea is another potential symptom that could begin around the second week of pregnancy. Some women experience nausea as early as two weeks, while others may not feel it until later in their pregnancy. This nausea may be triggered by certain smells or foods and is most common during the first trimester.
6. Frequent Urination
At two weeks pregnant, frequent urination may start to occur. This symptom tends to become more noticeable as pregnancy progresses. Initially, it happens because of pregnancy hormones and changes in your body, including a growing uterus. As your baby grows, the pressure on your bladder will increase, making frequent bathroom trips common.
What Happens During Your Second Week of Pregnancy: Baby’s Development
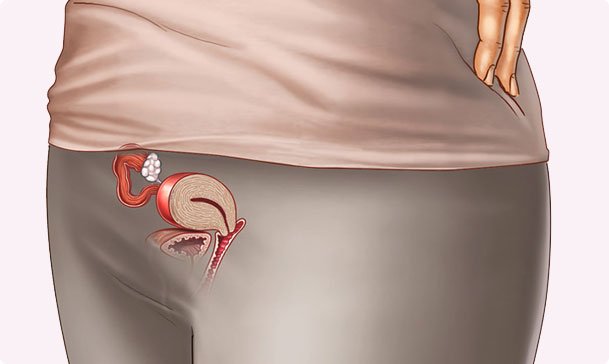
In the second week of pregnancy, which is roughly two weeks after ovulation and conception, your fertilized egg begins to divide and implant into your uterus. At this point, the baby is a small embryo measuring around 0.04 to 0.06 inches long.
Pre-Conception Phase: Your ovary releases an egg, which travels down the fallopian tube to meet sperm. If the sperm fertilizes the egg, conception occurs. This is known as ovulation, typically happening between days 10-14 of your menstrual cycle.
Post-Conception Phase: After fertilization, the zygote (fertilized egg) travels to the uterus, where it begins to divide into a blastocyst. The blastocyst consists of cells that will form the embryo and the placenta. The inner cells form the baby, and the outer cells help form the sac that surrounds and protects the baby.
Symptoms and Changes to Expect in the Second Week of Pregnancy:
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy hormones like HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) will start increasing significantly, leading to early symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and changes in appetite.
Breast Changes: Tender, swollen breasts are another sign of early pregnancy, although this may not be noticeable until later.
Cramps: Mild cramps can occur due to implantation and changes in your body as it adjusts to pregnancy.
What to Do During Week 2 of Pregnancy
While the second week of pregnancy is early, it’s still a good idea to start taking prenatal vitamins, stay hydrated, and avoid any substances that could harm your developing baby. Begin tracking your symptoms and consider taking a pregnancy test for confirmation once you’ve missed your period.
Conclusion: Early Pregnancy Symptoms at Two Weeks
The second week of pregnancy is a crucial time for early fetal development. Even though you may not have major symptoms, fatigue, spotting, and nausea are common signs that indicate pregnancy. By understanding the symptoms and changes that occur in your body during this stage, you can be more in tune with your pregnancy journey.
As your pregnancy progresses, you’ll continue to experience changes in your body. It’s important to stay informed and seek medical advice to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.