Hemorrhoids Treatment Guidelines: Your Complete Guide to Relief and Prevention
Hemorrhoids treatment, also known as piles treatment, focuses on relieving pain, reducing swelling, and preventing recurrence. Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus that can cause discomfort, bleeding, and itching. They are common among adults, but with the right approach, you can manage symptoms effectively and improve your quality of life.
This guide covers everything you need to know about hemorrhoids treatment — from understanding the types of hemorrhoids to the best medical and home remedies, plus proven prevention tips.
Understanding Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are classified into three main types:
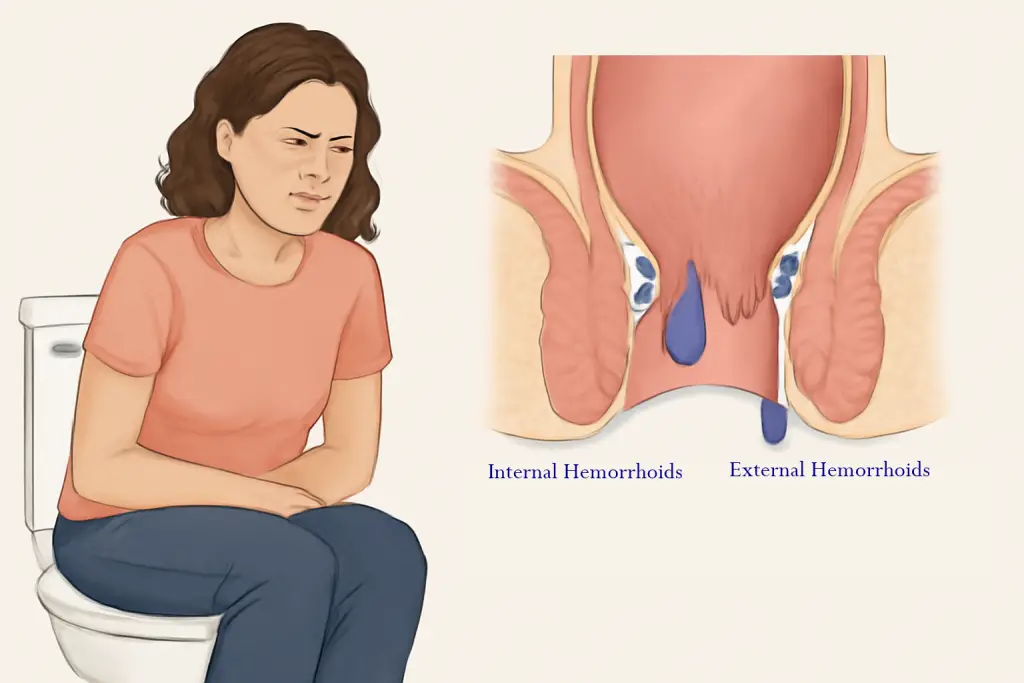
1. Internal Hemorrhoids
- Located inside the rectum
- Usually painless but may cause bleeding during bowel movements
- Common symptoms: painless bleeding, prolapse (hemorrhoid protruding outside), and mucus discharge
2. External Hemorrhoids
- Found under the skin around the anus
- Can be painful, especially if a clot forms (thrombosed hemorrhoids)
- Symptoms include itching, swelling, pain, and bleeding
3. Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
- Caused by blood pooling in an external hemorrhoid and forming a clot
- Can cause severe pain and swelling
Hemorrhoids Treatment Options
Treatment ranges from simple lifestyle adjustments to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Increase Fiber Intake: Eat 25–30 grams of fiber daily from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to soften stools and reduce straining
- Stay Hydrated: Drink 6–8 glasses of water daily to keep stools soft
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity stimulates healthy bowel movements
- Improve Bathroom Habits: Avoid straining, limit toilet time, and respond promptly to the urge to pass stool
2. Over-the-Counter Medications
- Topical Treatments: Creams or ointments with hydrocortisone or witch hazel can relieve itching and pain
- Oral Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or aspirin can help reduce pain and inflammation
- Stool Softeners: Such as docusate sodium, to ease bowel movements
3. Non-Surgical Procedures
- Rubber Band Ligation: Cuts off blood supply to the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and fall off
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of a chemical solution to shrink hemorrhoids
- Infrared Coagulation (IRC): Uses infrared light to coagulate tissue
- Cryotherapy: Freezing hemorrhoids to reduce size
4. Surgical Options
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Complete removal of large or severe hemorrhoids
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: Repositions hemorrhoids and reduces blood supply with less pain than traditional surgery
- Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (DGHAL): Locates and ties off feeding arteries
How to Prevent Hemorrhoids
- Eat a high-fiber diet to keep bowel movements regular
- Drink plenty of water to soften stools
- Exercise regularly to promote healthy digestion
- Avoid delaying bowel movements and minimize straining
- Take breaks from sitting if you have a desk job
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pelvic vein pressure
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids are common and can significantly impact daily comfort, but effective treatment is available. Early intervention through hemorrhoids treatment options — including lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures — can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Always consult a healthcare professional for a tailored treatment plan to achieve the best results.
source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15120-hemorrhoids